Diagnostic Kit for Quantification of Hepatitis B Virus DNA (PCR-Fluorescence Probing)

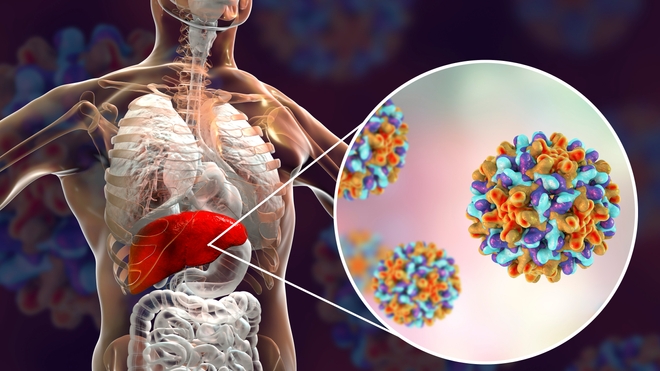
A diagnostic kit for quantification of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) DNA using PCR-Fluorescence Probing is a molecular diagnostic tool designed to detect and measure the amount of HBV DNA in a patient's blood or other biological samples. This type of diagnostic kit is commonly used in clinical laboratories for the diagnosis and monitoring of Hepatitis B infection.
Here's a general overview of how such a kit might work:
Sample Collection: A blood sample or other relevant biological material is collected from the patient suspected of having Hepatitis B.
2. Nucleic Acid Extraction: The HBV DNA needs to be extracted from the collected sample. This step involves breaking open the cells and separating the genetic material (DNA) from other components of the sample.
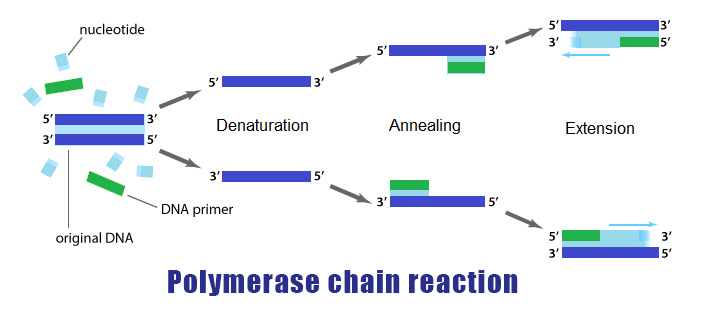
3. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification: PCR is used to amplify specific regions of the HBV DNA. It helps to make millions of copies of the target DNA, making it easier to detect and quantify.
4. Fluorescence Probing: This step involves the use of specific fluorescent probes that are designed to bind to the amplified HBV DNA segments. These probes emit fluorescent signals when they bind to the target DNA, making it possible to measure the amount of HBV DNA present in the sample.
6. Quantification: The amount of HBV DNA in the sample is determined by measuring the fluorescence signals emitted during the probing step. The intensity of the fluorescence is directly proportional to the concentration of HBV DNA in the sample.
7. Data Analysis: The data obtained from the fluorescence detection is processed and analyzed using specialized software, which converts the fluorescent signals into quantitative results, expressing the viral load in terms of HBV DNA copies per milliliter (copies/mL) of the sample.